Angioplasty procedures are used to open blocked arteries and restore blood flow to and from the heart. As people age, their arteries may harden, become clogged, or narrow, affecting the ability of blood to flow through the body and potentially placing people at an increased risk of blood clots, which can lead to heart attack or stroke. This hardening of the arteries is known as arteriosclerosis.
Angioplasty procedures are a gentle way of breaking down the blockage to open the arteries and allow blood to flow unobstructed through them. They can be performed on the coronary arteries, located near the heart, or peripheral arteries, located in other parts of the body.
Coronary heart disease: a common age-related illness
Angioplasty procedures are usually done to treat severe atherosclerosis, a specific type of arteriosclerosis in which plaque builds up inside the arteries and limits the flow of blood to the vital organs and other parts of the body. That plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium and other substances found in the blood. Atherosclerosis can lead to serious problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
Treatment options
There are many treatment options for heart disease ranging from conservative treatment to open heart surgery. Lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise, quitting smoking and eating healthy are good ways to prevent and treat early coronary heart disease. Medication such as blood thinners and high blood pressure medication may be effective at relieving symptoms and lowering the risk of a heart attack. And, for more severe cases, surgical options such as angioplasty procedures or coronary artery bypass surgery are available.
Angioplasty: minimally-invasive treatment techniques
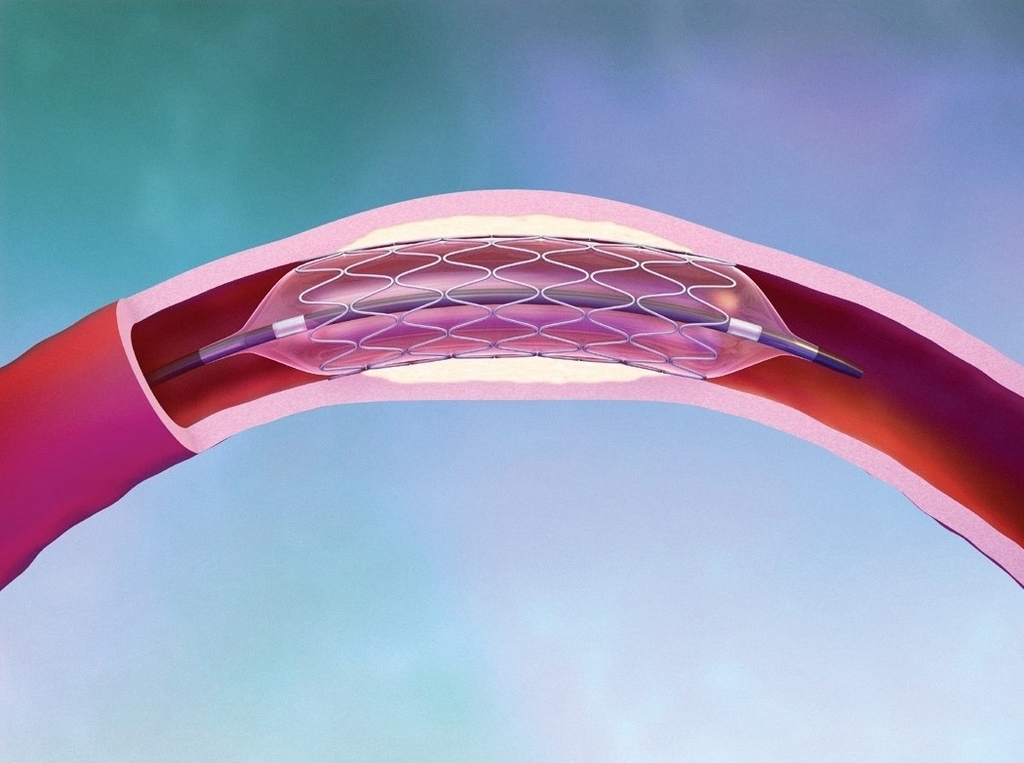
Angioplasty is a minimally-invasive procedure to re-open blocked arteries. It is performed via catheter, or a long, narrow tube inserted via an artery in the groin, arm or wrist.
There are many types of angioplasty procedures which may be performed alone or in conjunction with each other, including balloon dilation, stenting and rotablation.
In rotablation, the cardiologist uses a tiny drill at the tip of the catheter to cut away the plaque lining the artery walls. The bits of plaque that remain can be easily swept away by the bloodstream and absorbed in the body.
In balloon dilation, the cardiologist inflates a small medical balloon inside the artery to expand the artery walls and break down plaque.
With stenting, the specialist implants a tiny tube-shaped device called a stent to hold the newly-expanded arterial walls open. Stents may be made from metal wire or artificial materials. In some procedures, the stent may be coated in medicine, which it will slowly release into the bloodstream over a long period of time in order to prevent the return of atherosclerosis.
Rotablation cuts away excess plaque, while balloon dilation and stenting push the plaque up against the artery walls. German heart specialists are typically trained in a variety of procedures and can choose which option is best for each individual case.
Who is a candidate for angioplasty procedures?
Angioplasty is a type of minimally-invasive heart procedure with fewer risks than open heart surgery. Patients who are not good candidates for open heart surgery may be able to benefit from minimally-invasive procedures such as types of angioplasty. In addition, even otherwise-healthy patients can benefit from shorter recovery times, less risk of complications and fewer anesthesia-related risks. The treatment usually involves an overnight stay in the hospital, and patients can often go home the next day.
Still, for people with advanced coronary heart disease, angioplasty procedures may not be enough to remove all the plaque from the arteries to resume normal blood flow. In particularly advanced cases, coronary bypass surgery may be a more effective treatment option. Only a trained heart specialist can determine the severity of each case and make a treatment recommendation based on what they observe.
Risks and complications
Common complications of catheter-assisted procedures include bleeding or bruising where the catheter was inserted or blood vessel damage from the catheters. For angioplasty procedures, there is a very small risk of developing restenosis, arrhythmia, a heart attack or stroke.
Our partner hospitals at Premier Healthcare Germany have special cardiac catheterization labs where minimally-invasive heart procedures are regularly performed by highly experienced cardiologists. Contact us for more information on cardiac procedures in Germany.